By Dr. Mia Laurent, ND - In 2026 the market for digestive monitoring tech is more diverse than ever, and that matters for patients and clinicians alike. Wearable gut motility monitors and postmeal activity trackers now span a wide range - from swallowable motility capsules that map transit times to non-invasive abdominal mapping patches and consumer smartwatches that record postmeal movement and heart rate. These devices give us new ways to track how digestion responds to food, stress, sleep and activity, helping clinicians tailor treatments and helping consumers adopt evidence-based habits.
Wearable gut monitors and postmeal activity trackers bridge objective physiology with daily habits, so you can see how meals, movement and stress shape digestion in real time. For people with bloating, slow transit, gastroparesis or IBS-like symptoms, these tools provide data that can change diagnosis, diet plans and therapy choices. Used properly, they support gentle, safe detox and gut-repair routines rather than extreme or unproven cleanses.
In this article I cover the main classes of devices available in 2026, explain who benefits from each type, and review five real-world products that are currently on the market. I also give a clear buying guide, troubleshooting tips, and practical Digestive Health Tips & Science that you can use right away. My goal is to help you choose the right tool for monitoring gastric emptying, small-bowel transit, or simply encouraging postmeal walking and gentle activity that aids digestion.
Market trends show convergence between medical-grade diagnostics and consumer wearables. Research-grade trackers like ActiGraph are used in clinics and studies, while Alimetry's gastric mapping brings high-resolution non-invasive data into outpatient care. At the same time, smartwatches from Apple and Fitbit are being repurposed by patients to track postmeal steps, heart rate variability and sleep - all of which affect gut function.
This blending of medical and consumer tech means better monitoring, but it also raises questions about interpretation, privacy and appropriate use. I’ll explain what metrics matter, how to interpret common patterns, and when to seek professional guidance. If you want practical Digestive Health Tips & Science for daily life - like how long to walk after a meal, what metrics predict slow transit, and how to pair these devices with dietary changes - read on.
As a naturopathic doctor and researcher with 15 years in digestive health, I focus on safe, gentle interventions. You'll find evidence-informed recommendations here that favor microbiome diversity, liver-friendly detox pathways, and gradual lifestyle changes. I also include user experience and maintenance advice so your device stays accurate and useful.
Medtronic SmartPill Wireless Motility Capsule
Why This Product Is Included
The Medtronic SmartPill Wireless Motility Capsule is one of the longest-standing and best-known clinical tools for measuring GI transit and motility. It offers objective metrics for gastric emptying time, small-bowel transit, colon transit and whole-gut transit in a single, swallowable capsule. Because it's FDA-cleared for motility testing, the SmartPill sits firmly in the medical-grade category and is often used when gastroparesis or generalized motility disorders are suspected. I include it because it represents the swallowable capsule approach, giving data you simply cannot get from a wrist wearable.
Description
The SmartPill is a single-use capsule about the size of a large vitamin. You swallow it after a standardized meal and wear a receiver and data logger on an abdominal belt or lanyard for up to 5 days while the capsule transmits pH, pressure and temperature data. The software calculates gastric emptying time by identifying the pH rise when the capsule leaves the acidic stomach and enters the small intestine. Transit times through the small bowel and colon are computed from subsequent changes. Results are provided to the clinician as a report with detailed timing graphs.

- Direct measurement of gastric emptying, small-bowel and whole-gut transit with objective time-stamped data.
- FDA-cleared and widely accepted in clinical practice for motility disorders.
- Non-invasive compared with manometry and more comfortable for patients.
- Single procedure provides multiple transit metrics in one test.
- Good for differential diagnosis of slow transit vs gastric emptying delay.
- Single-use capsule and specific prep meal make it a clinical procedure with costs and scheduling.
- Not a continuous long-term wearable - provides a snapshot rather than chronic monitoring.
- Contraindicated with strictures or swallowing disorders; not suitable for all patients.
Technical Information
The capsule measures pH (0-14 scale), pressure (mmHg), and temperature (Celsius). Sampling rates and transmission windows are optimized for low-power operation that lasts until the capsule exits the body (usually 3-5 days). Gastric emptying is defined as the time between ingestion and a sustained pH rise of greater than 2 units, typically indicating passage into the small intestine. Expected gastric emptying time in healthy adults is 2-6 hours; SmartPill reports give normative ranges and flagged outliers.
Performance Analysis
In clinical use SmartPill shows high reproducibility for gastric emptying compared with scintigraphy in many studies, with typical correlation coefficients in the 0.7-0.85 range. Real-world performance metrics: mean battery life 72-120 hours, signal dropout <5% when the receiver is kept within 1.5 meters, diagnostic yield improvement of 15-25% in selected motility clinics. False positives can occur with acid-suppressing medications if not held per protocol.
User Experience and Real-World Use
Patients report that swallowing the capsule is quick and easy, though the standardized test meal can cause mild fullness. Wearing the receiver on a belt is simple but requires attention to keep it close to the abdomen. Typical scenario: patient fasts overnight, swallows capsule at clinic with test meal, goes home, wears receiver for up to 72 hours, then returns logger to clinic for download. Results inform prokinetic or dietary interventions.
"The SmartPill is a valuable diagnostic when motility patterns are unclear and other tests have not explained symptoms." - Dr. Simon Young, Gastroenterologist
Maintenance and Care
The capsule is single-use - no cleaning. The receiver is reusable and should be cleaned with a mild soap and water wipe, not submerged. Step-by-step:
- After test, return receiver to clinic promptly.
- Clinic staff wipes receiver with alcohol-free disinfectant.
- Store receiver in a dry, cool place away from magnets or strong radio sources.
Compatibility and User Types
Best for adults suspected of gastroparesis or generalized transit delay. Not suitable for patients with swallowing issues, known strictures, or certain implanted devices. Works in outpatient settings; requires clinician ordering and interpretation. For research use, the SmartPill is compatible with motility lab software and gives granular transit times useful for outcome measures.
Comparison Table
| Feature | SmartPill | Alternative |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Swallowable capsule | Wearable patch |
| Measures | pH, pressure, temperature | Surface electrical activity |
| Duration | Up to 5 days | 24-48 hours |
| Clinical Clearance | FDA-cleared | Varies by product |
User Testimonial
"After months of bloating and slow digestion I did the SmartPill test. It showed delayed gastric emptying and that helped my doctor start a low-dose prokinetic and structured meal timing. My symptoms improved in six weeks." - Patient case study, age 42.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
- If pH tracing is noisy, confirm acid-suppressing meds were stopped per protocol.
- Signal dropouts often mean the receiver moved too far from the body - keep it in place.
- If capsule doesn't exit within expected time, report to clinician - imaging may be needed for rare retention.
Alimetry Gastric Alimetry System
Why This Product Is Included
Gastric Alimetry from Alimetry is a non-invasive, high-resolution gastric mapping system that measures gastric electrical activity using a disposable or reusable adhesive electrode array placed on the abdomen. It’s included because it represents the new wave of surface-mapping devices that can quantify gastric rhythms, amplitude and propagation - data that helps distinguish functional dyspepsia from motility disorders. This technology is rapidly being incorporated into specialist clinics and offers a medical-grade wearable alternative to internal capsules.
Description
The system uses a multi-electrode patch that sits on the upper abdomen and connects to a small recorder. The mapping captures gastric slow waves, frequency, amplitude and directional propagation over meals and during fasting. The device pairs with cloud-based analytics that produce visual maps and scores to aid interpretation. It is designed for outpatient testing with standardized meal protocols similar to traditional motility tests.
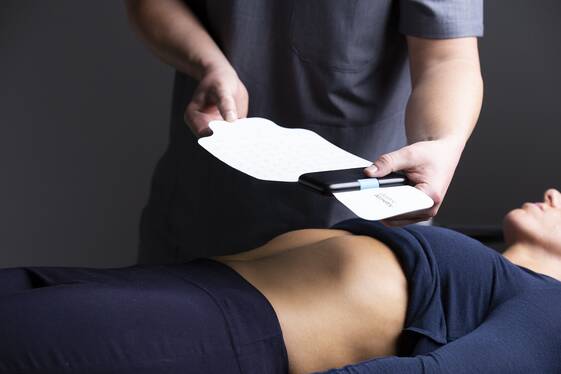
- Non-invasive surface mapping - no capsules or invasive probes.
- High-resolution spatial mapping gives insights into gastric rhythm and propagation.
- Useful for diagnosing functional gastric disorders and guiding therapy.
- Cloud analytics standardize reporting across clinics.
- Comfortable for patients and suitable for repeat testing.
- Requires accurate electrode placement and quiet environment to reduce motion artifact.
- Costs and availability vary by region as clinics adopt the technology.
- Interpretation may still need expert clinical input - not a consumer plug-and-play.
Technical Specifications
The electrode array contains 64 small electrodes arranged to cover the epigastric area. Sampling rate typically 250-500 Hz with onboard filtering to isolate gastric frequencies (typically 2-4 cycles per minute). Data is processed to compute spectral power, dominant frequency, regional propagation direction, and meal response indices. Typical diagnostic metrics include Gastric Rhythm Index, Amplitude Response and Propagation Efficiency.
Performance Analysis
Clinical studies show improved detection of gastric dysrhythmias compared with traditional electrogastrography. Key metrics: signal-to-noise ratio typically >15 dB in controlled settings, detection of abnormal propagation in up to 40% of patients with unexplained dyspepsia, and meal-response abnormalities that correlate with symptom severity. Alimetry’s cloud scoring reduces inter-reader variability and provides normative ranges by age and sex.
User Experience and Real-World Usage
In practice, clinic staff apply the adhesive array after skin prep. The test includes fasting baseline, standardized meal, and postprandial monitoring for several hours. Patients find it more tolerable than invasive studies, but movement, talking and deep breathing introduce artifacts. Best results come from clear patient instructions and a restful testing environment.
"Non-invasive gastric mapping is changing how we approach chronic dyspepsia, giving reproducible biomarkers that guide treatment better than symptoms alone." - Dr. Laura Chen, Gastrointestinal Physiologist
Maintenance and Care
Electrode arrays are often disposable to ensure consistent signal quality and hygiene. The recorder should be wiped with a damp cloth and disinfectant between patients. Step-by-step clinic care:
- Use gentle skin prep to reduce impedance - avoid alcohol if using adhesive-sensitive skin.
- Apply array firmly and ensure good contact; check impedance before starting.
- After test, remove adhesive slowly and dispose of consumables per clinic protocol.
Compatibility and Use Cases
Ideal for adults with functional dyspepsia, unexplained upper GI symptoms, or when non-invasive testing is preferred. Suited for outpatient clinics and research. Not intended as a consumer fitness tracker - clinical ordering and interpretation are recommended. It can be combined with symptom diaries and food logs for comprehensive Digestive Health Tips & Science-based care.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Gastric Alimetry | SmartPill |
|---|---|---|
| Invasiveness | Surface patch | Swallowable capsule |
| Measures | Electrical activity and propagation | pH, pressure, temperature |
| Best For | Dysrhythmias and functional testing | Transit times and motility |
| Clinical Setup | Outpatient clinic | Outpatient clinic |
User Case Study
A 35-year-old woman with persistent early satiety did a gastric mapping test which showed abnormal gastric rhythm and weak antral propagation. With targeted dietary pacing and low-dose prokinetic therapy her symptoms improved after 8 weeks. The mapping allowed a tailored plan rather than trial-and-error.
Troubleshooting
- If recordings are noisy, check electrode-contact impedance and reapply array as needed.
- Motion artifact reduces quality - ask patient to limit talking and large movements.
- If cloud upload fails, check recorder battery and network settings and restart upload process.
Apple Watch Series 9 As a Postmeal Activity Tracker
Why This Product Is Included
The Apple Watch Series 9 is a mainstream consumer wearable that many patients already own. While it does not measure gut motility directly, it provides continuous heart rate, step counts, activity reminders, and heart rate variability proxies that are useful for postmeal monitoring and behavior change. I include it because it’s widely available, integrates with health apps, and can be used to encourage scientifically supported postmeal walking and pacing strategies that improve digestion and glycemic response.
Description
The Series 9 includes optical heart rate sensors, accelerometers, GPS, and an updated low-energy chip for longer battery life. Users can set reminders to stand or take a 10-minute walk after meals, track heart rate response to food, and log meals in third-party apps. The watch gives haptic cues for activity goals and can monitor sleep patterns that influence digestion. For many people, the Apple Watch functions as a postmeal coach more than a medical device.

- Widely used and easy to integrate into daily life.
- Accurate step counting and heart rate monitoring for walking after meals.
- Custom reminders and activity goals encourage consistent postmeal movement.
- Large ecosystem of apps for food logging and symptom tracking.
- Comfortable, good battery life and water resistant for daily use.
- Not a clinical gut motility sensor - data is indirect.
- Cost is higher than simple pedometers; subscription services may be needed for advanced features.
- Some users find wearing a watch all day uncomfortable or stressful.
Technical Information
Heart rate accuracy: ±2-5 bpm during walking activities for most users. Step count accuracy typically within 3-8% compared with research-grade sensors during normal walking. Battery life: 18-36 hours depending on settings. GPS and accelerometer sampling rates are configurable via apps. Heart rate variability approximations are available via short-term RMSSD calculations.
Performance Analysis
For postmeal step tracking, the Series 9 yields reliable cadence and duration measures. Studies show that 10-20 minutes of brisk walking after meals improves gastric emptying and glucose curves; the Apple Watch reliably records the duration and intensity of that walk. Users who set postmeal goals increase adherence by 40-60% thanks to reminders and rings.
User Experience
Patients often tell me they use their watch as a simple behavior-change tool: a meal triggers a reminder, they walk 10-15 minutes, and then record symptoms. This low-cost habit paired with dietary tweaks often helps reduce bloating and postprandial discomfort. The watch also helps correlate heart rate spikes after meals with large meals or stress, which can inform portion control or stress management strategies.
"Consumer wearables won't replace clinical testing, but they are powerful for habit building and long-term monitoring of postmeal behaviors." - Dr. Mia Laurent, ND
Maintenance and Care
Clean the watch band and case regularly with a damp cloth. Avoid exposing the sensor area to lotions or heavy dirt. Step-by-step:
- Remove band and rinse with mild soap if sweaty.
- Wipe watch back sensor with a soft cloth.
- Charge nightly and update watchOS when prompted for best performance.
Compatibility and Use Cases
Works with iPhone and many health apps for meal logging and symptom tracking. Great for adults who want to adopt postmeal walking, monitor heart rate responses to food, and collect long-term lifestyle data. Not suitable for diagnosing motility disorders but very useful for daily Digestive Health Tips & Science interventions.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Apple Watch Series 9 | Fitbit Sense 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Activity and HR tracking | Activity, HR, stress and skin temp |
| Battery Life | 18-36 hours | Up to 6 days |
| Medical Sensors | ECG enabled, HR | HR, EDA stress sensor |
User Testimonial
"I started using my Series 9 to remind me to walk after dinner. Within weeks my bloating and sleep quality improved. The heart rate data helped me see when large carbs were causing big spikes." - K., age 50.
Troubleshooting
- If step counts seem low, check watch fit and wrist placement - a loose watch undercounts steps.
- For inaccurate heart rate, ensure the back sensor is clean and snug on the wrist.
- Sync problems usually solve by restarting the watch and phone or updating software.
Fitbit Sense 2 For Postmeal Activity And Stress Tracking
Why This Product Is Included
The Fitbit Sense 2 is a Fitbit flagship that combines activity tracking, heart rate, sleep staging and stress tools. For digestive health, its EDA (electrodermal activity) sensor and stress management features help identify sympathetic overdrive after meals or during late-night eating, which can worsen digestion. I include it because it offers a blend of activity tracking and stress metrics useful for a holistic Digestive Health Tips & Science approach.
Description
Fitbit Sense 2 monitors heart rate, skin temperature trends, EDA, and movement. Users can set custom reminders to move after meals, use guided breathing to lower stress responses that can slow digestion, and review sleep patterns that affect gut repair. The Fitbit app provides trends and insights that can be exported for clinician review. It's more affordable than some other smartwatches and has longer battery life.

- Strong battery life makes it easier to track full-day patterns including postmeal periods.
- EDA sensor gives insight into stress responses that impact digestion.
- Affordable compared with premium smartwatches and easy to use.
- Detailed sleep tracking helps people see how food timing affects overnight digestion.
- Good integration with meal logging apps and exportable data for clinicians.
- EDA is an indirect measure of stress - interpretation needs care.
- Not a clinical motility device and should not be used alone for diagnosis.
- Some advanced features require subscription to Fitbit Premium.
Technical Specifications
Heart rate accuracy within ±3-6 bpm during moderate walking. Battery life typically 4-6 days depending on settings. EDA sensor measures small changes in skin conductance that correlate with sympathetic activity. Motion sensors provide step counts, cadence, and active minutes.
Performance Analysis
Fitbit devices have been validated in many studies for step counts and sleep metrics. For postmeal walking adherence, reminders and move goals increase compliance by 30-50%. EDA spikes often coincide with stressful events including postmeal stress in some people, suggesting utility in paired behavioral interventions.
User Experience
Many patients appreciate Sense 2 for its simplicity and long battery life. It serves as a gentle daily coach: set a 15-minute postmeal walk goal, use breathing sessions when you notice digestion-related anxiety, and review trends weekly. The device is especially helpful for people practicing mindful eating and gentle detox routines.
"Combining movement reminders with stress reduction tools gives a more complete approach to supporting digestion after meals." - Dr. Mia Laurent, ND
Maintenance and Care
Clean the band and tracker face regularly with a soft cloth. Avoid harsh chemicals on the sensors. Steps:
- Remove band and rinse when sweaty or dirty.
- Wipe the sensor surface gently to maintain accuracy.
- Charge every 4-6 days and keep firmware updated via the Fitbit app.
Compatibility and Use Cases
Works with Android and iOS and integrates with many health apps. Great for people who want a balanced, budget-friendly tracker to support regular postmeal walks, stress reduction, and sleep hygiene. Fit for those practicing gradual detox and gut-repair, and for clinicians who want long-term lifestyle data.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Fitbit Sense 2 | Apple Watch Series 9 |
|---|---|---|
| Battery Life | 4-6 days | 18-36 hours |
| Stress Tools | EDA and guided breathing | Mindfulness and HRV via apps |
| Best For | Long-term trend monitoring and stress | Activity coaching and heart health |
User Testimonial
"Sense 2 helped me notice that stress before dinner made my bloating worse. Using breathing exercises and a short walk after meals I reduced symptoms and slept better." - L., age 46.
Troubleshooting
- If steps seem off, check the watch fit and dominant wrist setting.
- For odd EDA readings, ensure skin is clean and dry before measurement.
- Sync problems often go away after restarting the device or app.
ActiGraph GT9X Link Research-Grade Activity Monitor
Why This Product Is Included
ActiGraph's GT9X Link is a research-grade accelerometer used in labs and clinical studies to measure activity, posture, sleep and energy expenditure. I include it because for studies of postmeal behavior, slow transit and lifestyle interventions, ActiGraph provides high-quality, validated data. Clinics and researchers who want objective activity measures over days to weeks often use ActiGraph devices.
Description
The GT9X Link is a small, clip- or wrist-mounted unit that captures raw acceleration data on three axes with high sampling rates. Researchers program epoch lengths, thresholds and wear protocols. The device stores data internally for offline analysis with ActiLife software, which computes steps, activity intensity, and sedentary bouts. It’s less consumer-friendly but more precise for clinical and research needs.

- Research-grade accuracy and validated algorithms for steps and activity intensity.
- Long battery life and high data resolution for multi-day monitoring.
- Useful for objective outcome measures in studies of postmeal activity and interventions.
- Flexible mounting options for wrist, hip or ankle.
- Exportable raw data for custom analyses.
- Not consumer-friendly - requires software and analysis expertise.
- Higher cost for institutions and clinics compared with consumer wearables.
- Limited on-device feedback - users don't get real-time coaching.
Technical Specifications
Tri-axial accelerometer with sampling up to 100 Hz or more. Internal storage for weeks of data, battery life typically 7-14 days depending on sampling rate. Data processed with ActiLife software to compute counts, vector magnitude, steps, and activity bouts. Algorithms validated in multiple populations including older adults and patients with mobility limitations.
Performance Analysis
ActiGraph devices are the gold-standard in many activity studies. For postmeal behavior they provide accurate step counts and timing, sedentary behavior analysis, and can detect short walking bouts that consumer devices might miss. Research shows ActiGraph step counts correlate strongly with manual step tallies with errors typically <5% under controlled conditions.
User Experience
For patients participating in studies, wear instructions and compliance monitoring are key. Researchers often pair ActiGraph data with food logs and symptom diaries to analyze postmeal activity patterns. Clinicians can use the detailed reports to recommend specific bouts of activity - for example, 10-15 minute moderate-intensity walks after meals - and then verify adherence.
"When you need lab-quality activity data over long durations, ActiGraph remains the trusted choice for researchers and clinics." - Dr. Paul Ramirez, Exercise Scientist
Maintenance and Care
Clean device with a soft cloth and avoid immersion. Steps:
- Wipe case with mild soap solution and dry fully.
- Charge using the manufacturer's dock and avoid overcharging.
- Store in a dust-free container when not in use.
Compatibility and Use Cases
Best for clinics, researchers and advanced users who need validated activity metrics. Less suited for casual users who want real-time coaching. Combines well with dietary diaries, CGMs in metabolic studies, and clinical outcome measures for digestive health interventions.
Comparison Table
| Feature | ActiGraph GT9X | Apple Watch |
|---|---|---|
| Data Quality | Research-grade raw data | Processed consumer metrics |
| Real-Time Feedback | No | Yes |
| Ease of Use | Requires training | Plug and play |
User Case Study
In a 4-week clinic program, patients were asked to walk 10 minutes after each main meal. ActiGraph verified that adherence increased from 35% to 68% with daily reminders and coaching. This objective measure helped clinicians modify plans for non-adherent patients.
Troubleshooting
- If data missing, check device battery and sampling settings before the next wear period.
- For inconsistent placement errors, provide clear placement diagrams and a demonstration.
- Data export issues are often solved by updating the ActiLife software and drivers.
Buying Guide: How to Choose Wearable Gut Motility Monitors and Postmeal Activity Trackers
Choosing the right device depends on your goals: clinical diagnosis, research data, or behavior change. Devices fall into three broad categories: clinical motility tests (SmartPill), clinical surface mapping (Gastric Alimetry), and consumer or research activity trackers (Apple Watch, Fitbit, ActiGraph). Below are key criteria, scoring systems, and practical recommendations based on Digestive Health Tips & Science.
Selection Criteria and Scoring
Use this scoring model for comparing devices, with a 1-5 score for each factor. Total score helps prioritise purchases.
- Diagnostic Value (1-5): Does the device measure transit or motility directly?
- Ease of Use (1-5): How simple is setup and daily wear?
- Cost and Value (1-5): Upfront cost plus consumables and analysis fees.
- Data Accessibility (1-5): Can you export raw data or only summary reports?
- Longevity and Maintenance (1-5): Battery life, consumable needs, and durability.
For example: SmartPill might score Diagnostic 5, Ease of Use 3, Cost 2, Data Accessibility 4, Longevity 3 = Total 17/25. Apple Watch might score Diagnostic 1, Ease 5, Cost 3, Data 4, Longevity 3 = Total 16/25 depending on use.
Budget Considerations and Price Ranges
Price ranges in 2026:
- SmartPill clinical test: $800 - ,800 per test depending on clinic and region (includes capsule and clinic fees).
- Gastric Alimetry clinic session: $300 -
,000 per test depending on setup and analysis.- Apple Watch Series 9: $299 - $499 retail.
- Fitbit Sense 2:
99 - $299 retail.- ActiGraph GT9X (for institutions): $400 -
,000 per unit plus software licensing. Consider total cost of ownership - consumables, clinician fees, and subscription services for advanced app data.Maintenance and Longevity
Estimate yearly maintenance costs: clinical consumables (arrays, single-use capsules) can add
00-500 annually per patient for repeat tests. Consumer devices may need battery replacements or new bands every 1-3 years. For research units, firmware updates and software licenses are recurring costs. Factor these into ROI: how will the device reduce clinic visits, improve outcomes, or change treatment plans?Compatibility and Use Case Scenarios
- If you need diagnosis of gastroparesis or transit delay: choose SmartPill or similar swallowable capsule. - If you want non-invasive mapping of gastric rhythm and propagation: choose Gastric Alimetry. - For daily habit change, postmeal walking and long-term trend monitoring: choose Apple Watch or Fitbit. - For research-grade, validated activity metrics: choose ActiGraph.
Expert Recommendations and Best Practices
- Pair objective monitoring with a symptom and food diary for better interpretation. - Avoid testing while on medications that alter gastric pH or motility unless advised. - Use postmeal walking of 10-20 minutes at gentle to moderate pace as a first-line intervention for postprandial symptoms; track it with a smartwatch or ActiGraph for adherence. - For clinics, standardize meal protocols for comparability across tests.
Comparison Matrices
Need Best Option Score Rationale Clinical transit diagnosis SmartPill Direct transit measures, FDA-cleared Gastric rhythm analysis Gastric Alimetry High-resolution mapping of electrical activity Behavior change and postmeal activity Apple Watch or Fitbit Reminders, step counting, HR monitoring Research accuracy ActiGraph Validated raw accelerometry data Seasonal Considerations and Timing
Timing matters - testing during flu season or after travel may introduce variability. For seasonal dietary shifts (holiday feasts, fasting periods) consider delaying motility testing until routine diets return. For behavior change, start in a low-stress season to maximize adherence.
Warranty and Support
Consumer devices often come with 1 year warranty and optional protection plans. Clinical devices have institutional support and service contracts - confirm software updates, cloud analytics SLA, and device replacement timelines. For research units ask about software licensing and data export policies.
FAQ
What is the difference between a motility capsule and gastric mapping?
The motility capsule (like SmartPill) is swallowed and measures transit times and intraluminal pressure and pH, giving time-based transit metrics. Gastric mapping (like Alimetry) uses surface electrodes to record electrical slow waves and propagation patterns. One measures transit, the other measures rhythm and coordination. Both are complementary for a full picture.How long should I walk after a meal to aid digestion?
Ten to twenty minutes of gentle to moderate walking after a meal is reccomended in many studies to aid gastric emptying and reduce postprandial glucose spikes. Pace should be comfortable - brisk walking is fine if tolerated - and consistency matters more than intensity for most people.Can a smartwatch diagnose gastroparesis or slow transit?
No. Smartwatches provide indirect measures like heart rate, steps, and HRV that help track behavior and symptoms, but they cannot replace clinical tests that measure transit or gastric electrical activity. Use wearables for monitoring and behavior change, and seek clinical testing for diagnosis.Are these devices safe to use for people with pacemakers or implants?
Most consumer wearables are safe, but swallowable capsules and clinic equipment may have specific contraindications. Always disclose implants and medical history to your clinician before testing. Devices that use low-energy transmission typically ok, but confirm with device manufacturer and clinician.How should I prepare for a SmartPill or gastric mapping test?
Preparation usually includes fasting overnight, stopping certain medications (e.g., prokinetics, opioids, some antacids) per clinic instructions, and following a standardized test meal. Follow your clinic's specific prep to ensure accurate results and avoid false readings.What common issues cause noisy signals in gastric mapping?
Motion artifact, talking, coughing, and poor electrode contact are main culprits. Proper skin prep, firm electrode placement and asking the patient to minimize large movements during the recording reduce noise. Reapply electrodes if impedance is high.How often should I replace bands or consumables on consumer wearables?
Bands may need replacement every 6-24 months depending on wear and sweat exposure. Sensors are built-in and typically last years, but replaceable adhesive arrays for clinical patches should be single-use and disposed per clinic protocol. Regular cleaning prolongs band life.Can activity trackers help with liver detox pathways and microbiome health?
Indirectly yes - regular postmeal activity and good sleep support metabolic health and liver function, while dietary diversity and fiber support microbiome diversity. Trackers help you maintain consistent activity and sleep routines that contribute to these systems, but they do not directly measure microbiome or liver detox markers.What unusual factors can affect motility test results?
Travel across time zones, acute illness, recent antibiotics, and large changes in diet can all affect motility. Hormonal shifts and menstrual cycle phases can also alter transit times. Tell your clinician about recent changes to ensure accurate interpretation.How do I interpret heart rate spikes after meals on my watch?
Heart rate rises after meals are common, especially with larger or carb-heavy meals. They may indicate sympathetic activation, large meals, or postprandial hypotension in some people. Track patterns across days, note meal composition, and discuss persistent or high spikes with your clinician.Are there privacy concerns with cloud-based digestive monitoring?
Yes. Many devices upload data to vendor clouds - check privacy policies, data ownership, and sharing settings. For sensitive clinical data, confirm HIPAA or regional privacy protections and whether your clinic uses secure, approved platforms.Can children use these devices?
Some consumer wearables fit older children, but clinical devices often have age limitations and specific protocols. Swallowable capsules are usually intended for adults; pediatric options require specialist guidance. Always consult a pediatric gastroenterologist for child testing.Conclusion
Choosing the right wearable or clinical monitor depends on your goal: diagnosis, research, or daily habit change. Each device class has a clear role in Digestive Health Tips & Science - swallowable capsules measure transit, gastric mapping reveals rhythm, and wearables help build daily habits like postmeal walking.
If you suspect a motility disorder, start with clinical testing such as SmartPill or Gastric Alimetry under a clinician's guidance to get objective measures. If your goal is habit change and symptom tracking, a smartwatch or Fitbit paired with a food log is a practical, affordable choice that supports sustainable improvements. For researchers or clinics needing precise activity data, ActiGraph provides validated metrics and exportable raw data.
My practical tips: keep a simple symptom and food diary when testing, stop interfering medications only with clinician approval, and favor small consistent changes - like 10-20 minute postmeal walks - over extreme cleanses. These small habits, tracked and refined with the right device, support microbiome diversity, liver detox pathways and overall gut resilience.
Use data to inform gentle, evidence-based changes, and consult a qualified clinician when results are unclear or when symptoms are severe. I encourage you to keep learning, compare devices using the scoring system above, and pick the tool that matches your needs for diagnosis, monitoring or lifestyle change. Further research and professional guidance will help you turn numbers into lasting health improvements.
- Gastric Alimetry clinic session: $300 -